
PATENT: DETECTION OF ANALYTES BY ENZYME-MEDIATED STRAND DISPLACEMENT REACTIONS
The subject invention pertains to composition and methods of using said composition as an in vitro biosensor of small molecules in biological and/or environmental samples using enzyme-assisted nucleic acid reactions. The methods and compositions can be used to sense and/or transduce the signal of a sensing event mediated by allosteric proteins, endonucleases and nucleic acid reactions. This invention allows the rapid development and setup of one-pot assays to provide results in minutes. The methods and compositions may be used to generate an electrochemical, fluorescent, colorimetric, and/or luminescent output and the methods can be performed in different modalities, including a solution- based or paper-based assay.
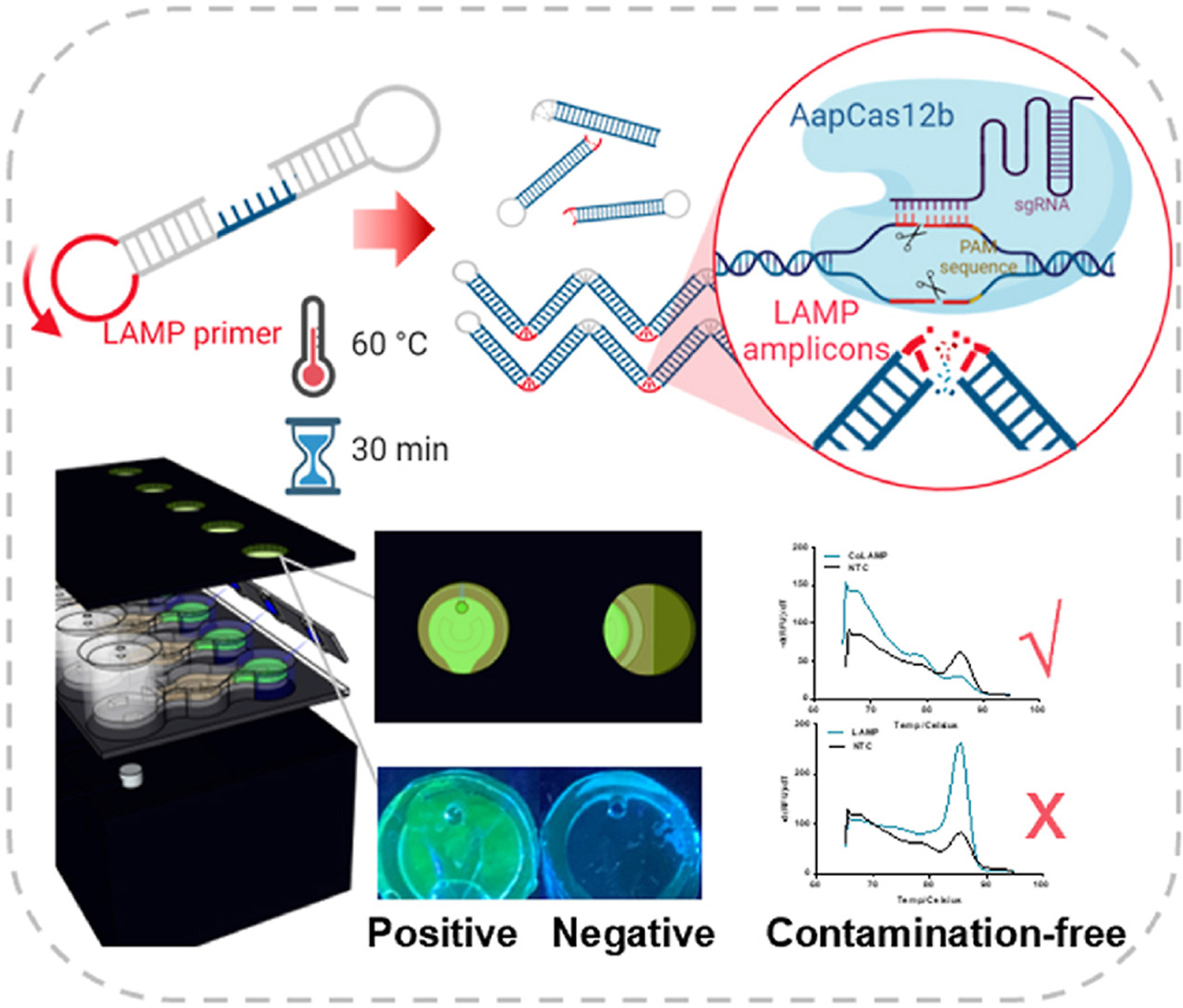
CoLAMP: CRISPR-based one-pot loop-mediated isothermal amplification enables at-home diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 RNA with nearly eliminated contamination utilizing amplicons depletion strategy
Rapid point-of-care diagnostics, essential in settings such as airport on-site testing and home-based screening, displayed important implications for infectious disease control during the SARS-CoV-2 outbreak. However, the deployment of simple and sensitive assays in real-life scenarios still faces the concern of aerosol contamination. Here, we report an amplicon-depleting CRISPR-based one-pot loop-mediated isothermal amplification (CoLAMP) assay for point-of-care diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 RNA. In this work, AapCas12b sgRNA is designed to recognize the activator sequence sited in the loop region of the LAMP product, which is crucial for exponential amplification. By destroying the aerosol-prone amplifiable products at the end of each amplification reaction, our design can significantly reduce the amplicons contamination that causes false positive results in point-of-care diagnostics. For at-home self-testing, we designed a low-cost sample-to-result device for fluorescence-based visual interpretation. As well, a commercial portable electrochemical platform was deployed as a proof-of-concept of ready-to-use point-of-care diagnostic systems. The field deployable CoLAMP assay can detect as low as 0.5 copies/μL of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in clinical nasopharyngeal swab samples within 40 min without the need for specialists for its operation. Read More >
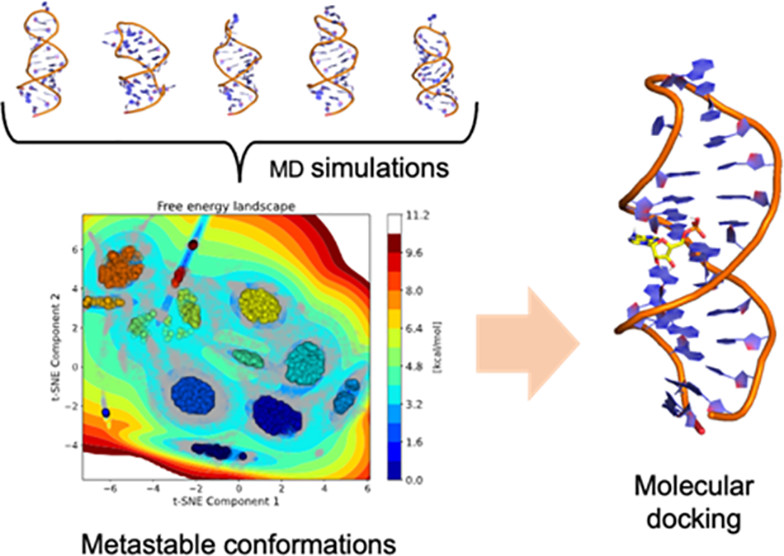
Prediction of Aptamer–Small-Molecule Interactions Using Metastable States from Multiple Independent Molecular Dynamics Simulations
Understanding aptamer–ligand interactions is necessary to rationally design aptamer-based systems. Commonly used in silico tools have proven to be accurate to predict RNA and DNA oligonucleotide tertiary structures. However, given the complexity of nucleic acids, the most thermodynamically stable conformation is not necessarily the one with the highest affinity for a specific ligand. Because many metastable states may coexist, it remains challenging to predict binding sites through molecular docking simulations using available computational pipelines. In this study, we used independent simulations to broaden the conformational diversity sampled from DNA initial models of distinct stability and assessed the binding affinity of selected metastable representative structures. Read More >
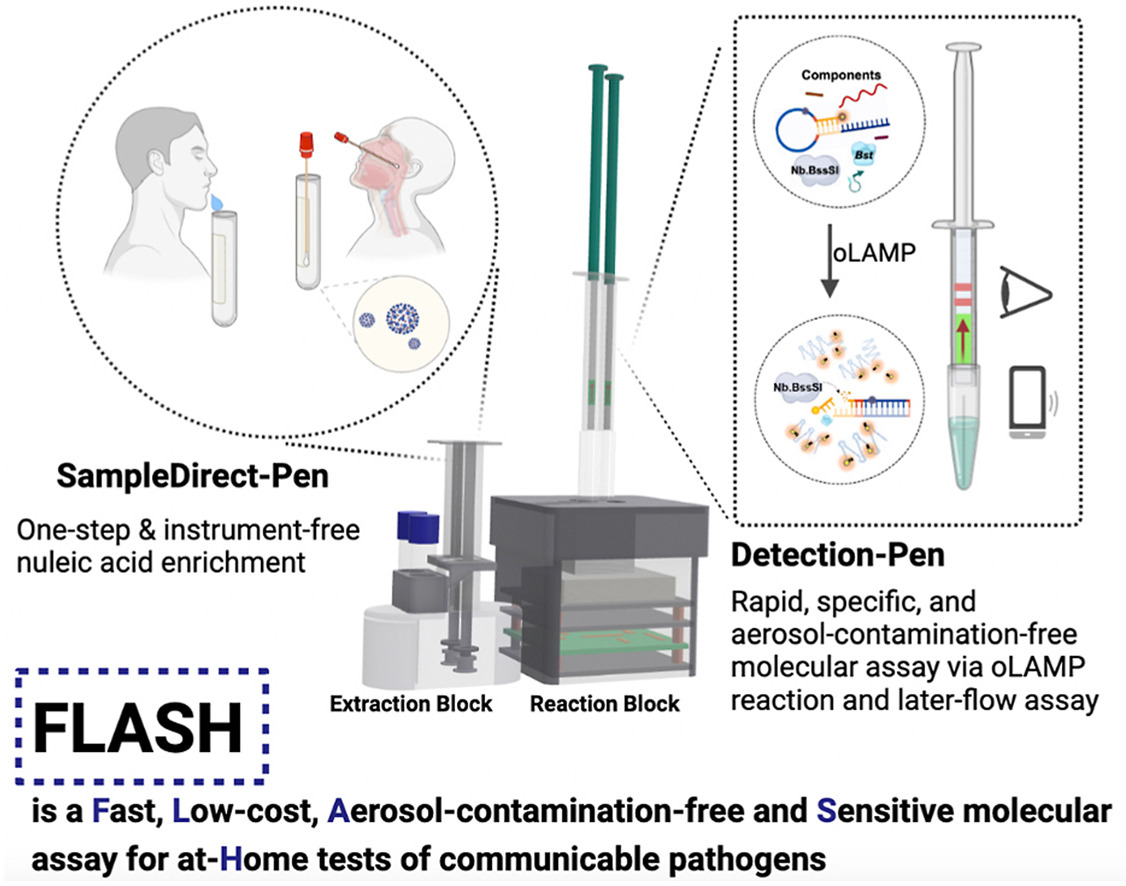
Disposable and low-cost pen-like sensor incorporating nucleic-acid amplification based lateral-flow assay for at-home tests of communicable pathogens
Highlights: A Fast, Low-cost, Aerosol-contamination-free, and Sensitive molecular assay for at-Home tests (FLASH). The lateral flow-based FLASH enabled Covid-19 testing achieving a sensitivity as low as 0.5 copies/μL. Complete accuracy in comparison to the qPCR in samples mimicking 11% of prevalence. A simplified sample-to-result workflow of FLASH with a total assay time in 20–30 min. Pen-like devices and the miniaturized FLASH platform readily for untrained user. Read More >
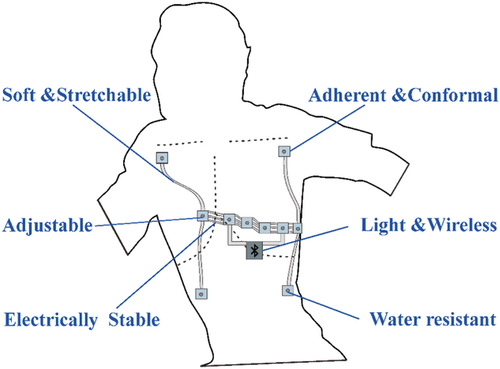
Highly Stretchable and Skin Adhesive Soft Bioelectronic Patch for Long-Term Ambulatory Electrocardiography Monitoring
Wearable devices offer a revolutionary approach to ambulatory electrocardiography (ECG) for cardiovascular disease diagnosis. Herein, an adhesive, highly stretchable and conformal (ASC) patch for long-term ambulatory ECG monitoring is presented. The ASC patch is designed with a “three-bridge” structure to provide inhomogeneous strain distribution during stretching. Meanwhile, the electrical stability is achieved by stretchable liquid metal interconnects at the domain experiencing larger strain. Read More >
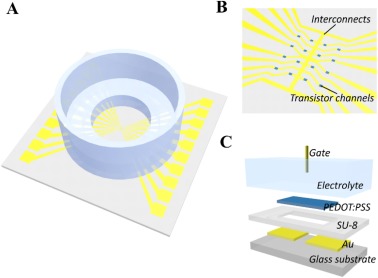
Organic electrochemical transistor array for monitoring barrier integrity of epithelial cells invaded by nasopharyngeal carcinoma
Organic electrochemical transistor was used to distinguish epithelial/cancer cell types based on transconductance spectrums. Results showed that the novel nasopharyngeal cancer cells NPC43 demonstrated distinct morphology and invasive properties. Our OECT array was able to spatially map cancer/epithelial cell co-culture patterns based on 100-Hz transconductance. This multi-channel OECT array could be a complementary tool to optical imaging for studying cancer cell-cell interactions. Read More >